
One of the most severe pathologies of the musculoskeletal system is coxarthrosis of the hip joint. If a visit to a medical institution is delayed, the disease can develop - to the appearance of an acute pain syndrome that cannot be relieved by analgesics and the complete loss of motor ability of the joint.
In this article, we will talk in detail about all the nuances of eliminating the consequences of this pathological process, its stages and preventive procedures.
What is coxarthrosis of the hip joint?
We are talking about a severe form of degenerative-dystrophic disease of the hip joint, which can lead to a violation of the functional ability of the joint, even its absolute loss. In terms of frequency of manifestation, coxarthrosis ranks second after deforming arthrosis of the knee joint.
Coxarthrosis of the hip joint is accompanied by degenerative cartilage damage, the appearance of pathological growths, bone resorption, inflammatory processes and other complications.
That is, this pathology is characterized by damage to the entire joint, including cartilage tissue, synovial layer, subchondral bone plate, muscle structures, capsules and ligaments.
The following forms of the disease are also distinguished:
- Primary coxarthrosis. It is considered the most common disease in the hip joint. In elderly people, this pathology manifests itself against the background of age-related changes;
- Secondary coxarthrosis. It manifests itself as a result of any disease.
Causes of coxarthrosis
The development of pathology can be caused by external, acquired and hereditary reasons.
In particular, coxarthrosis can manifest itself against the background of congenital weakness of the hip joint, degenerative-dystrophic changes, trauma, inflammatory processes, bone marrow necrosis of the femoral head, metabolic disorders, genetic factors, age-related changes, obesity. , vascular anomalies and working in difficult conditions.
It should be noted that almost all joint structures are subject to inflammation.
3 stages of development of coxarthrosis of the hip joint
During the development of the pathological process, the viscosity of the joint fluid increases, which leads to the appearance of microcracks and causes dehydration of the cartilage surface. This, in turn, contributes to the appearance of stiffness and limited mobility. A person feels such unpleasant manifestations during daily stress and physical activity. As the pressure in the lower extremities increases, the exhausted joint adapts to the forced state and begins to destroy nearby structures.
Currently, there are 3 stages of disease development:
- First. At this stage, coxarthrosis of the hip joint has mild symptoms that are inconsistent and visible in the affected area. At the same time, motor activity is preserved and it is enough to take medicine to relieve pain;
- Second. When the patient is diagnosed with coxarthrosis of the hip joint in the 1st stage, the disease does not cause much concern, but when it comes to the 2nd stage of the disease, the symptoms are more obvious. The pain gets stronger and starts spreading to other parts of the body. Motor ability deteriorates significantly, which is especially noticeable after a long walk or increased physical effort;
- the third. If coxarthrosis of the hip joint of the 2nd degree can still be treated, in the third stage the pathology becomes chronic. It is accompanied by constant pain and is transmitted to the lower part of the body. The patient loses the ability to move without crutches. In the absence of appropriate therapeutic measures, atrophy of cartilage and muscle structures occurs.
Types of coxarthrosis
The classification of the pathology of the hip joint is based on one criterion - how the disease occurs in the musculoskeletal system. There are two main risk factors that trigger the onset of the disease - genetic and acquired as a result of age-related changes. The pathological process is also divided into several types depending on the source of occurrence:
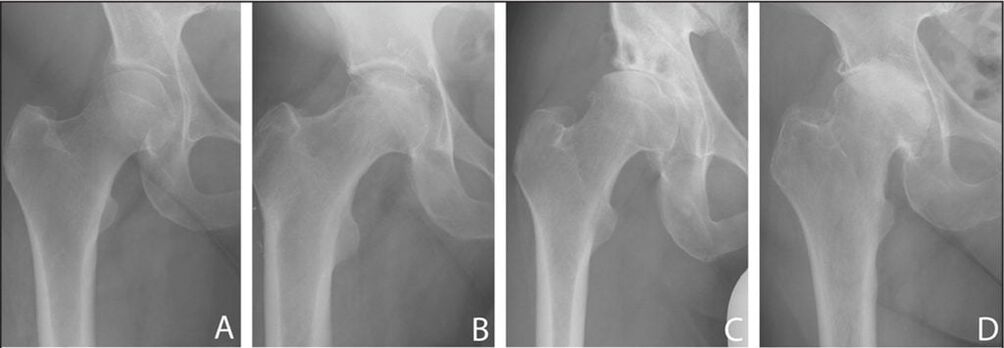
- Primary coxarthrosis. This pathology manifests itself in the hip area and is acquired. At the initial stage, it affects the synovial capsule, after which it moves to the area of tissues surrounding the joint. Risk factors include increased pressure on the pelvic bones, excessive physical activity, and the presence of inflammatory foci in the lower extremities and spine. Degenerative lesions are concentrated in tissues that have already undergone changes;
- Secondary coxarthrosis. This anomaly is hereditary. It manifests itself in the joints and musculoskeletal system. The development of the pathological process can begin already in the womb after a woman receives an injury, as well as against the background of necrosis of the bone marrow of the femoral head.
Types according to the occurrence of coxarthrosis:
- Post-infection. It is determined by the presence of consequences after infectious diseases;
- Post-traumatic. Diagnosed during complications after limb damage;
- Hormonal. Occurs against the background of metabolic disorders or drug overdose;
- Attractive. It appears in people over 50 years old due to the aging of the body.
Diagnostic measures
If you suspect 1 or 2 degree coxarthrosis of the hip joint, you should do a full body examination before starting treatment. It is also important to consult an orthopedic doctor who will conduct an examination, recommend laboratory tests, and formulate an effective treatment plan. Typically, diagnostic measures are limited to the following procedures:
- Radiography. It allows to study the parameters of the space between the cartilages, to diagnose the presence of pathological growths, as well as to assess the condition of the femoral head;
- Ultrasonography. It allows to track the etiology of changes in bone structures and ligaments, as well as study the dynamics of the patient's condition and determine the degree of development of the anomaly;
- CT. It allows you to get more detailed information about the condition of the joints and tissues located near them;
- MRI. This method provides a detailed description of the condition of all structures of the hip joint.
Treatment of coxarthrosis of the hip joint
If the patient has been diagnosed with coxarthrosis of the hip joint of the 1st or 2nd degree, it is possible to achieve an effective result with conservative methods. Such therapy is prescribed to the patient individually and includes several techniques that have a positive effect only together. Thus, if the patient is diagnosed with coxarthrosis of the hip joint of the 1st or 2nd degree and the corresponding symptoms are observed, the following measures can be recommended:
- Use of drugs;
- Physiotherapy procedures;
- shock wave therapy;
- Physiotherapy.
In order to achieve positive dynamics using conservative methods, it is necessary to eliminate the causes that cause coxarthrosis of the hip joint. First of all, you should reduce body weight, this will reduce the joint load and minimize the possibility of further development of the degenerative-dystrophic process.
In addition, you should eliminate the use of tobacco products and increase physical activity, avoiding excessive exertion. To prevent the development of pathology, experts recommend the use of orthopedic devices (ortheses and bandages). They allow you to fix the joint firmly and provide the necessary support during physical activity.
Medicines
Medicines are also prescribed individually. As a rule, patients are recommended to take the following drugs:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. These drugs allow you to achieve a double effect: they relieve pain and eliminate the inflammatory process;
- Preparations containing chondroitin, glucosamine and collagen. They allow to activate regeneration processes in the cartilage;
- Steroid hormones. Drugs with a strong anti-inflammatory effect. It is used in cases where NSAIDs are not significantly effective;
- Muscle relaxants. Medicines that reduce muscle tone, which is a necessary condition to eliminate pain of increased intensity;
- Means that normalize blood circulationand improving the trophism of tissues located near the joint;
- Vitamin B. Complexes containing this vitamin are prescribed to improve nerve transmission, which is of particular importance when the endings are compressed by the affected structures.
In case of pain of significant intensity, periarticular blocks are also recommended. They are performed only in clinical settings under the supervision of professionals. In this case, special solutions containing steroid hormones and anesthetics are co-injected.
Gymnastics for coxarthrosis of the hip joint
Special exercises recommended for coxarthrosis of the hip joint are especially effective for restoring motor function and reducing muscle spasm. Thanks to the optimally selected load, it is possible to eliminate pain and increase the amplitude of movements. In addition, a properly designed complex allows preventing atrophic processes in muscles and eliminating spasms if pinched nerve endings are observed against the background of the disease.

Also, gymnastics for coxarthrosis of the hip joint helps improve blood flow in the affected area and allows you to speed up the recovery process.
When choosing exercises, the specialist should take into account the destruction of the hip joint and the physical condition of the patient.

Physiotherapy methods
Massage procedures and physiotherapy can have a specific analgesic, anti-inflammatory and decongestant effect. They also help maintain muscle tone in the limbs and prevent atrophic processes.
The following procedures are performed for anomalies of the hip joint:
- UHF;
- laser exposure;
- Ultrasound treatment;
- Magnetotherapy;
- Exposure to direct electric current with drugs;
- paraffin therapy;
- Phonophoresis.
The above treatment will have a positive effect only if the patient is diagnosed with coxarthrosis at the initial stage.
Shock wave therapy for coxarthrosis
Shock wave treatment for coxarthrosis of the first or second stage provides significant positive dynamics. For example, a course of 10-15 shock wave therapy procedures can reduce the negative manifestations characteristic of stage 2 pathology to the symptoms of the initial stage of the disease.
It is important to understand that only timely treatment sessions can provide the best recovery effect. At the same time, it will be possible to reduce the number of SWT procedures.
However, the main positive aspect when affecting the affected joint with shock waves is the ability to normalize blood circulation, which facilitates the accelerated supply of important nutrients involved in the regenerative processes to the various structures of the hip joint.
Moreover, as part of the implementation of shock wave therapy, it is possible to crush pathological bone growths, which contribute to significant irritation of articular tissues and prevent regeneration.
Physiotherapists and neurologists with professional experience work in the clinics. They perfectly know how to work with the latest physiotherapeutic methods, which include the shock wave method. In addition, specialists have the ability to work with modern equipment. This gives a guaranteed positive effect and allows to shorten the treatment period.
Surgery
Unfortunately, many patients delay contacting a medical institution and turn to a specialist only when irreversible processes begin to occur in the hip joint.
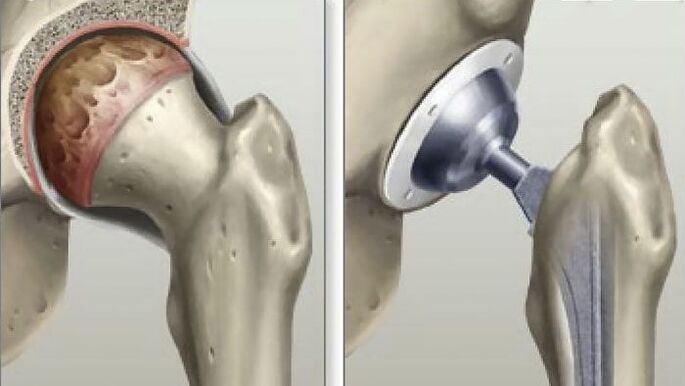
For advanced third or fourth stages of the disease, the only effective method is surgical intervention. This will restore motor ability and relieve acute pain, which means it will significantly improve the patient's quality of life.
As a rule, the operation is prescribed in the following cases:
- Painful sensations of increasing intensity that cannot be eliminated by drugs;
- lack of inter-articular space;
- Violation of the integrity of the femoral neck;
- Significant limitation of physical activity.
Taking into account the intensity of joint damage and changes in bone tissue, patients can be prescribed the following types of interventions:
- Arthrodesis. Interference causing complete immobility of the joint. Special metal plates are used for this purpose;
- Osteotomy. Surgical intervention consisting of artificial fracture of the femur to correct its axis. The resulting parts are placed in the most optimal position, which allows to remove excessive load from the affected joint;
- Arthroplasty. The only method possible to restore all functionality of the hip joint and achieve a complete recovery of the patient. After using this method to eliminate coxarthrosis, a person forgets about joint problems for 20-30 years.
Medical centers perform hip joint surgeries of any complexity. They are carried out by highly qualified specialists using modern tools and technology, which eliminates any errors during the intervention.
Complications of the disease
When the pathological process is at an advanced stage, the mobility of the joints is significantly limited, the person loses the ability to walk and take care of himself, pathological fusion of tissues is observed. Moreover, such an anomaly can have an undesirable effect on gait, which is associated with the appearance of lameness and a decrease in the size of the limb.
Preventive measures
Patients with pain in the hip joint should be observed by a specialist and should use special orthopedic devices during work and physical activity. In addition, it is necessary to undergo x-rays 3 times a year to monitor the condition of the joint after the operation.

















































